RESULTS
Patients
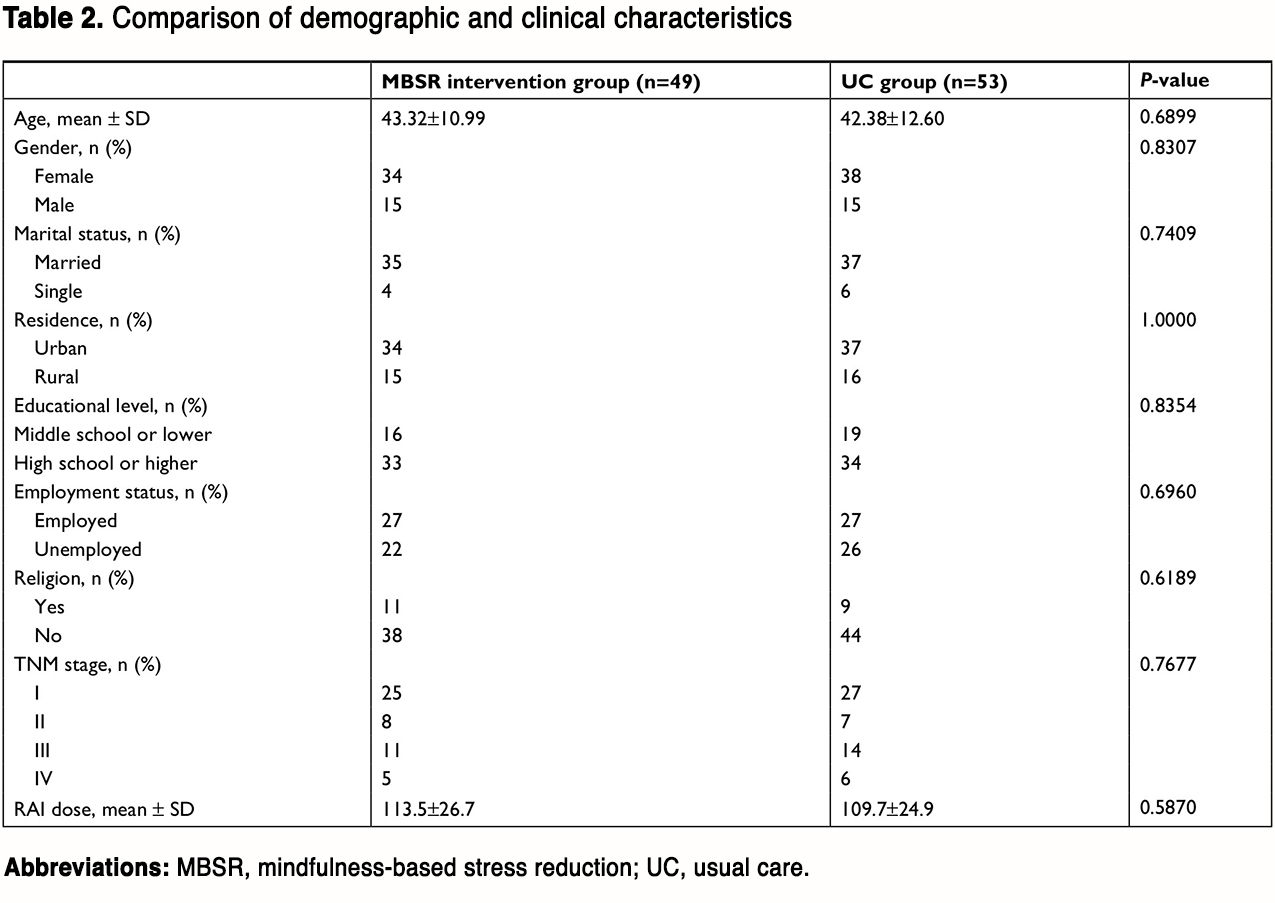
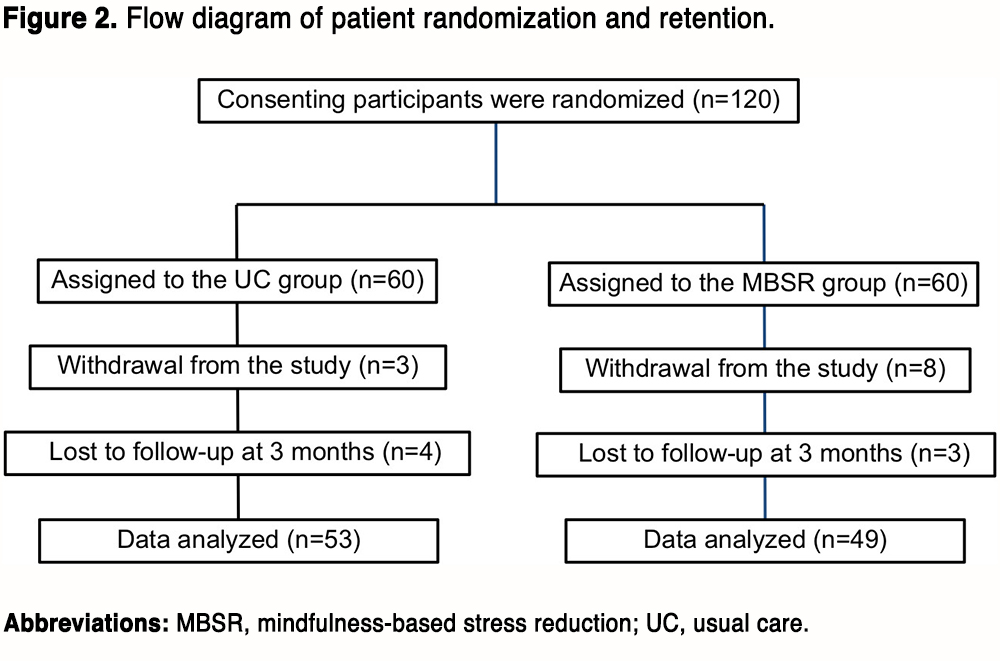
Figure 2 shows an overview of the number of subjects who were randomized and retained. In total, 18 patients (15%) dropped out before the end of this study, resulting in 53 patients in the UC group and 49 patients in the MBSR group for data analysis. The demographic information of the included patients is summarized in Table 2. There were no statistical differences in age, gender, marital status, residence, educational level, employment status, religion, TNM stage, and radioiodine dose between the two groups (all P<0.05).
(To view a larger version of Table 2, click here.)
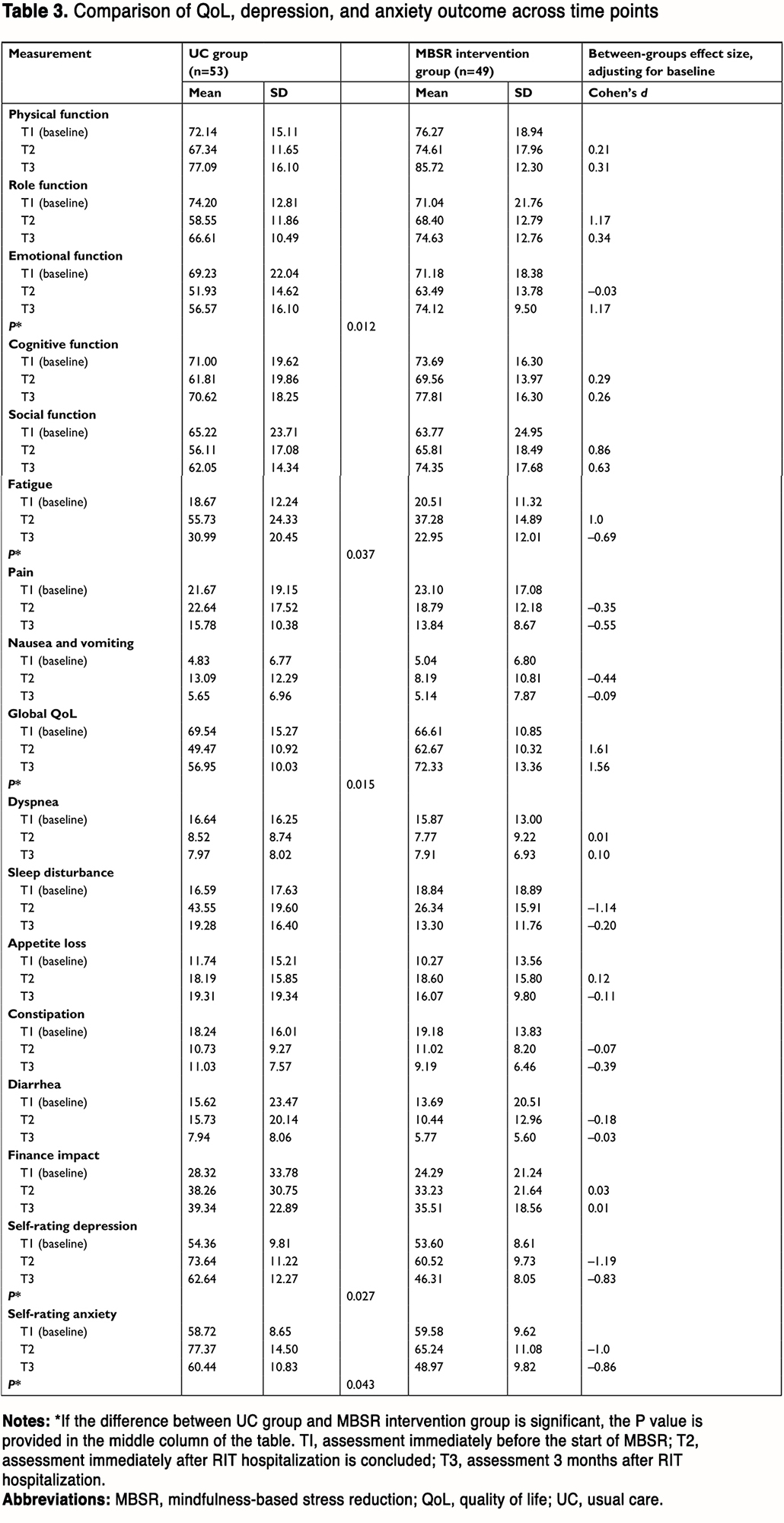
Linear mixed models were used to test the efficacy of MBSR on each QoL, SDS, and SAS. Descriptive data for each outcome are summarized in Table 3.
(To view a larger version of Table 3, click here.)
Health-related QoL
Statistically significant QoL improvements were observed in patients in the MBSR group through the 3-month period. Patients randomly assigned to the MBSR group showed significantly greater improvements in emotional function (P=0.012, d=–0.03 for T2 and d=1.17 for T3), fatigue (P=0.037, d=1.00 for T2 and d=–0.69 for T3), and global QoL (P=0.015, d=1.61 for T2 and d=1.56 for T3).
SDS and SAS
Patients randomly assigned to the MBSR group demonstrated greater scale improvement in depression (P=0.027, d=–1.19 for T2 and d=–0.83 for T3) and anxiety (P=0.043, d=–1.00 for T2 and d=–0.86 for T3).